We present Being-M0.5, the first real-time, controllable vision-language-motion model (VLMM), trained on the million-scale HuMo100M dataset to support random instructions, initial poses, long-term generation, unseen motions, and part-aware motion control.
Abstract
Human motion generation holds significant potential for real-world applications. Despite recent advancements, existing vision-language-motion models (VLMMs) remain limited in achieving this goal. In this paper, we identify the lack of controllability as a critical bottleneck, where VLMMs struggle with diverse human commands, pose initialization, generation of long-term or unseen cases, and fine-grained control over individual body parts. To address these challenges, we introduce Being-M0.5, the first real-time, controllable VLMM with state-of-the-art performance. Being-M0.5 achieves its controllability through training on HuMo100M, the largest human motion dataset to date, featuring over 5 million self-collected motions, 100 million multi-task instructional instances, and detailed part-level descriptions that address a long-standing gap in the field. Additionally, we propose a novel part-aware residual quantization technique for motion tokenization, enabling precise control over individual body parts during motion generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate Being-M0.5's superior performance across a wide range of motion benchmarks. Furthermore, we provide strategic design insights and a detailed time efficiency analysis to guide the development of practical motion generators.
Model Structure
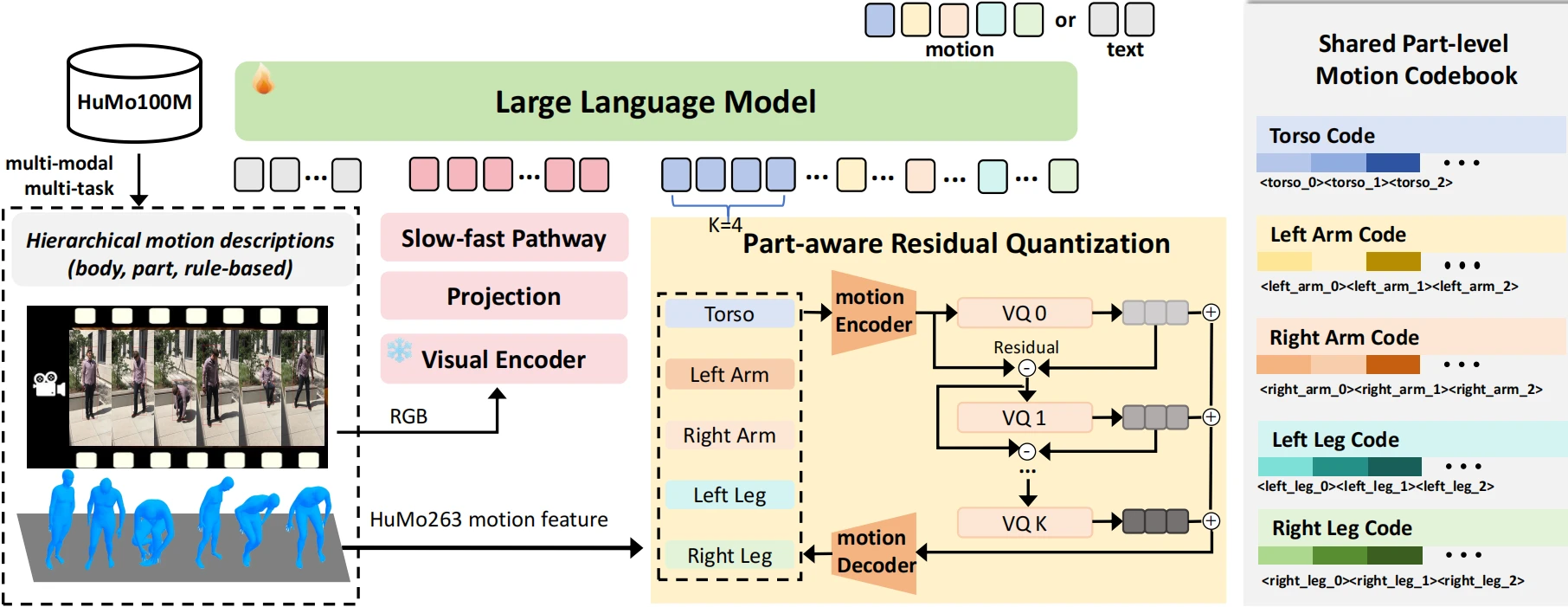
Being-M0.5 supports multi-modal inputs/outputs, built on a 7B LLM backbone. It employs SigLIP+2MLP for visual encoding and projection with a slow-fast strategy, alongside part-aware residual quantization for motion tokenization.
HuMo100M Dataset

We begin by collecting hundreds of millions of web videos. To ensure relevance to human activities, we apply a two-stage filtering process. First, keyword-based filtering removes videos lacking human-related text descriptors. Second, we employ YOLO to verify human presence through video tracking. We then use WHAM to extract SMPL parameters from the collected videos, regressing 3D human motion in world coordinates, and refine motion quality with the RL-based policy PHC.
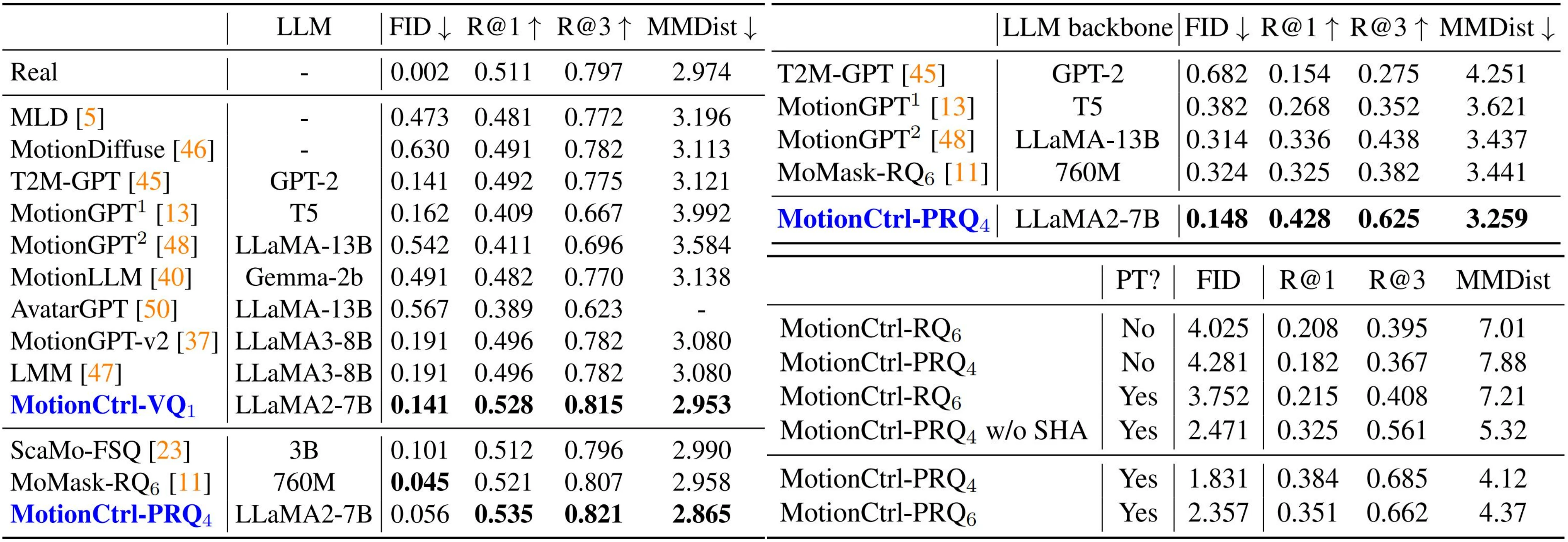
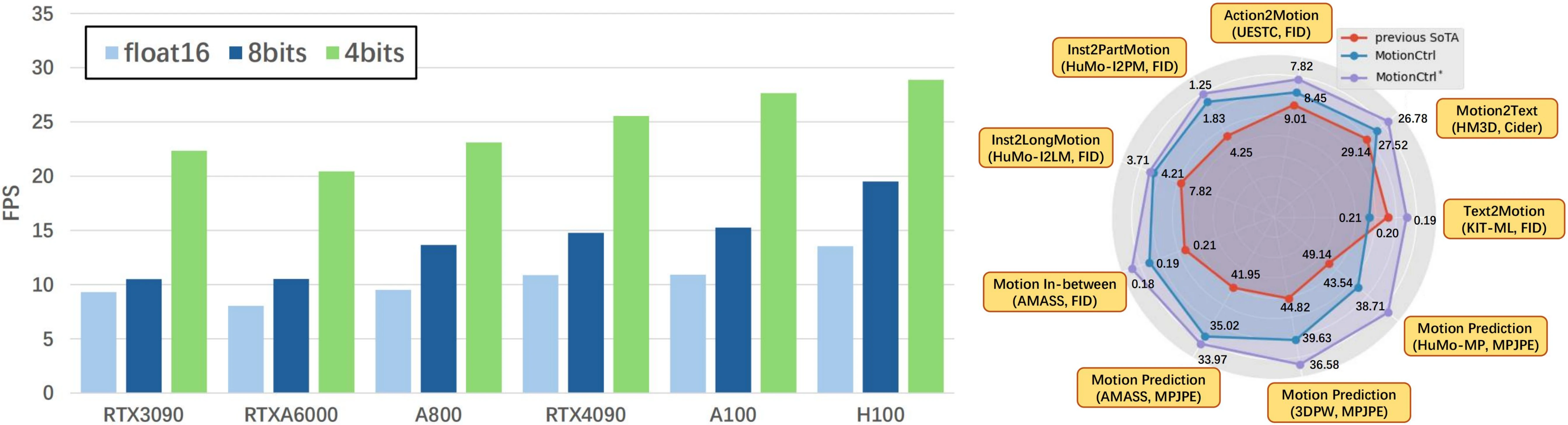
Experiments
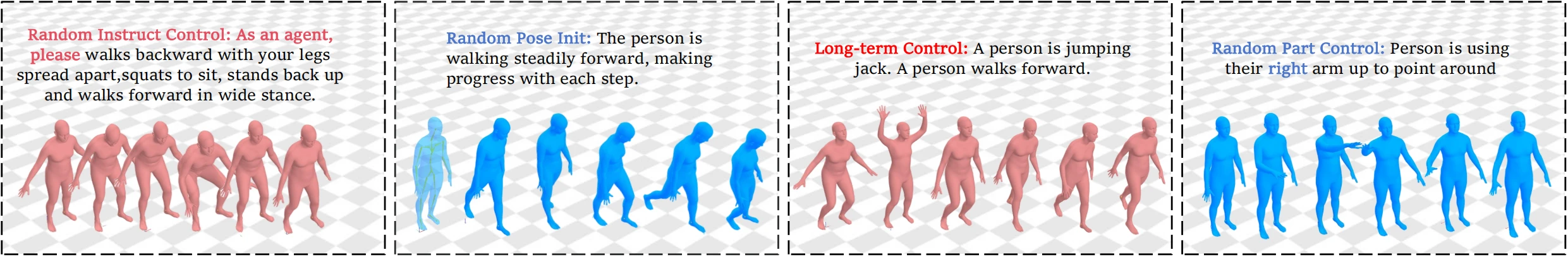
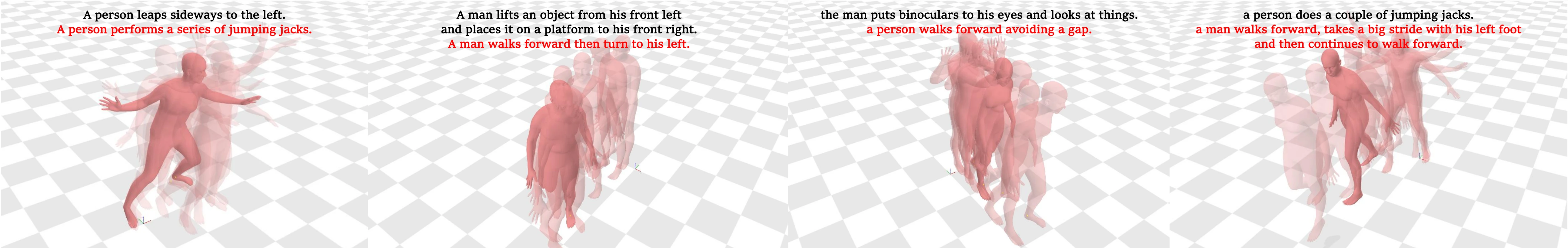
Example Cases

Citation
@inproceedings{cao2025real,
title={A Real-Time Controllable Vision-Language-Motion Model},
author={Cao, Bin and Zheng, Sipeng and Wang, Ye and Xia, Lujie and Wei, Qianshan and Jin, Qin and Liu, Jing and Lu, Zongqing},
booktitle={ICCV},
year={2025}
}